Creating Accessible Teaching and Learning Materials

One of the core values of the University of Manchester’s vision and strategic plan is a commitment to equality, diversity and equal opportunities for all. As such, we are committed to making teaching and learning accessible and inclusive. This article looks at:
- Why it is important to create accessible teaching and learning content.
- Provides links to guidance on how to make content more accessible, including tips on how to put that guidance into practice.
Why is it important to create accessible teaching and Learning Materials?
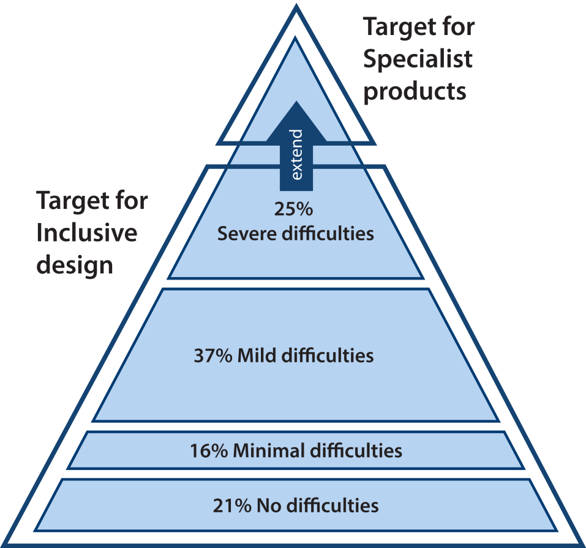
Wherever possible, we recommend using accessible and inclusive design principles from the outset when developing your course materials. By designing materials to be accessible to students with severe difficulties (Accessibility-first), we include as many students as possible, whilst still recognising that specialist solutions will be required to extend accessibility in some cases.
Not sure where to start?
It is easy to feel overwhelmed and as a result not make any changes. You may find it useful, to start small and concentrate on improving the types of content you use most often in your teaching. Taking a little time to set up some templates which work for you now, could save you time in the future.
- Looking for quick tips? Check out the Digital Accessibility Quick Checklist.
- Looking for information on accessibility of existing tools? Check out Online teaching tools accessibility comparison
- Want to talk to us about creating digital teaching and learning materials? Contact the Faculty eLearning Team.
Check out the resources below which provide guidance and support to help you put these tips into practice.
Plain English
Think about the language that you use, when creating your teaching content. Using Plain English, makes your communication more accessible for all audiences.
Documents and slide
Video content
Check out the creating accessible videos article for information on the following:
- Why subtitles are important. Examples of where subtitles are automatically created and what to do if you need to add subtitles.
- Tips for creating your own videos from scratch.
Adding Alt Text
Alt text (alternative text) is text that’s added to an image to describe the image’s content. Alt text ensures that users with visual impairments receive the same value from the image as a sighted user.
- The Faculty of Humanities – resources on Alt text covers when to use Alt text, how to write Alt text and guidance on how to add Alt text in common applications (Word, Mentimeter, PowerPoint, Blackboard, Padlet and more).
Testing Content
Below are some tools to help test the accessibility of content that you create.
Common document formats
- Microsoft Accessibility Checker is a tool built into Microsoft products, that allows you to check the accessibility while you work. The tool can be useful when working in Word, PowerPoint or Excel. For example, the checker can highlight where content may be difficult for a screen reader to interpret and how to fix those issues.
Check your teaching content using Ally
Both Blackboard and Canvas have Ally tools which can help you check the accessibility of your content.
- What Blackboard Ally do? (advantages and disadvantages)
- Quick start guide for using Blackboard Ally
- Accessibility features in Canvas
- A guide to using Ally on Canvas
Web pages
If you need to create web pages for your teaching content, then you can check the accessibility of content using a Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool. The tool highlights common accessibility errors on web pages such as low contrast, missing alt text and incorrectly ordered headings.
Screenreaders
You can check the reading order of PowerPoint slides, using the inbuilt Microsoft Accessibility Checker. You can also check how your content may be interpreted by a screenreader, by downloading and usinging a free screen reader (see examples below):
- NVDA screen reader – For Windows PCs.
- Silktide screen reader – A screen reader that works with Chrome which allows you to experience your website with a range of simulated disabilities, including colour blindness and dyslexia.
Mathematical Notation
Below are some resources for staff creating teaching content using mathematical notation.
- HTML: MathJax and MathJax Accessibility
- LaTeX: It can be difficult to produce accessible content containing mathematical notation. Often LaTeX is output to PDF, which cannot be read by screenreaders. You may want to consider compiling LaTeX as HTML, using a compiler such as LaTeXML (guidance) or Pandoc (guidance) or lwarp (guidance)
- Blackboard Math Editor (MathType for Blackboard): Accessibility Features
- Microsoft Word (Linear format equations using UnicodeMath and LaTeX in Word)
An excellent and comprehensive guide to accessible maths is produced and maintained by University of York.
Further Information
- Working with disabled students at the University of Manchester
- Read the GOV.UK accessibility blog
- AbilityNet resources for creating accessible digital content
- Understanding new accessibility requirements for public sector bodies (GOV.UK)
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
- A guide for Higher Education providers: Supporting students with vision impairment during Covid-19 by Thomas Pocklington Trust (TPT), Guide Dogs and LOOK UK